MATHS IMPORTANT FORMULA Book Jee Mains & Advance 2023
Hello friends,
MATHS IMPORTANT FORMULA Book Jee Mains & Advance 2023 | Free PDFs of Topper’s Notes . If you are a student of class 11 or 12th and want to crack NEET exam, then given MATHS IMPORTANT FORMULA Book Jee Mains & Advance 2023 are the best resources to do this. As we know that MATHS is the basic subjects in NEET entrance exam which is held by NTA National test agency NEET (UG), or National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (Graduation). NEET exam is used for admission in MBBS and BDS collages as well as alternative or traditional medicine and nursing in India. Download MATHS Important Formula Book Jee Mains & Advance 2023 | Free PDFs of Topper’s Notes from the given links of Google drive.
Here we also have provided you the best MATHS Important Formula Book Jee Mains & Advance 2023. You can buy them for serious reading. MATHS Important Formula Book Jee Mains & Advance 2023 is very well known website for pdfdownload.in, so we have also provided links of some best notes available.
MATHS Important Formula Book Jee Mains & Advance 2023 he subject of MATHS will help you in preparing for your final exams. Your final exams in MATHS will be held in March or April. These MATHS pdf notes are short, neat and clean, colored, regularly updated, and according to the syllabus set by the CBSE board following NCERT guidelines. The notes are very useful for competitive exams like NEET, AIIMS, and ACT (American College Testing), etc…. Not only our Biology short notes are suitable for CBSE board students, but also for other state board students. If you want to get high marks in MATHS then you must study from these notes. To download MATHS syllabus notes please read this article till the end.
Download GK Notes
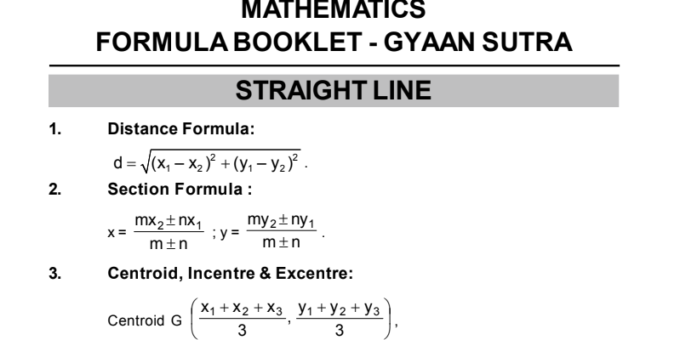
- Maths Algebra Notes PDF
- Maths Notes for Competitive Exams with Average Formulas
- General Science Questions For Competitive Exams Pdf
- 1000 Vocabulary Words with Meanings and Sentences PDF
- Maths Quantitative Aptitude Book PDF Free Download
- Basic English Grammar Exercises
- Arithmetic Maths
- Maths in PDF | Maths Tricks
- Number System in Maths
JEE Main Maths , Relations And Functions Questions With Solutions
Question 1: If A = [(x, y) : x2 + y2 = 25] and B = [(x, y) : x2 + 9y2 = 144], then A ∩ B contains _______ points.
Solution:
A = Set of all values (x, y) : x2 + y2 = 25 = 52
B = [x2 / 144] + [y2 / 16] = 1
i.e., [x2 / (12)2] + [y2 / (4)2] = 1.
Clearly, A ∩ B consists of four points.
Question 2: In a college of 300 students, every student reads 5 newspapers, and every newspaper is read by 60 students. The number of newspapers is ________.
Solution:
Let the number of newspapers be x.
If every student reads one newspaper, the number of students would be x (60) = 60x
Since every student reads 5 newspapers, the number of students = [x * 60] / [5] = 300
x = 25
Question 3: Let R be the relation on the set R of all real numbers defined by a R b if and only if |a − b| ≤ 1. Then R is __________.
Solution:
|a − a| = 0 < 1
Therefore, a R a ∀ a ∈ R
Therefore, R is reflexive.
Again a R b, |a − b| ≤ 1 ⇒ |b − a| ≤ 1 ⇒ b R a
Therefore, R is symmetric.
Again 1 R [½] and [½] R1 but [½] ≠ 1
Therefore, R is not anti-symmetric.
Further, 1 R 2 and 2 R 3, but 1 R 3 is not possible, [Because, |1 − 3| = 2 > 1]
Hence, R is not transitive.
Question 4: Let a relation R be defined by R = {(4, 5); (1, 4); (4, 6); (7, 6); (3, 7)} then R−1 o R is ________.
Solution:
First, find R−1.
R−1 = {(5, 4) ; (4, 1) ; (6, 4) ; (6, 7) ; (7, 3)}.
Obtain the elements of R−1 o R.
Pick the element of R and then of R−1.
Since (4, 5) ∈ R and (5, 4) ∈ R−1, we have (4, 4) ∈ R−1 o R
Similarly, (1, 4) ∈ R, (4, 1) ∈ R−1 ⇒ (1, 1) ∈ R−1 o R
(4, 6) ∈ R, (6, 4) ∈ R−1 ⇒ (4, 4) ∈ R−1 o R,
(4, 6) ∈ R, (6, 7) ∈ R−1 ⇒ (4, 7) ∈ R−1 o R
(7, 6) ∈ R, (6, 4) ∈ R−1 ⇒ (7, 4) ∈ R−1 o R,
(7, 6) ∈ R, (6, 7) ∈ R−1 ⇒ (7, 7) ∈ R−1 o R
(3, 7) ∈ R, (7, 3) ∈ R−1 ⇒ (3, 3) ∈ R−1 o R,
Hence, R−1 o R = {(1, 1); (4, 4); (4, 7); (7, 4), (7, 7); (3, 3)}.
Question 5: If
, then f [f { f (x) }] equals ________.
Solution:
f [ f (x) ] = (f (x) − 3)/ ( f (x) + 1)
Now f [f { f (x) }] = f ([3 + x] / [1 − x])
= 4x/4
= x
Therefore, f [f { f (x) }] = x.
Question 6: If f (x) = cos (log x), then find the value of f (x) * f (4) − [1 / 2] * [f (x / 4) + f (4x)].
Solution:
f (x) = cos (log x)
Let y = f (x) * f (4) − [1 / 2] * [f (x / 4) + f (4x)]
y = cos (log x) * cos (log 4) − [1 / 2] * [cos log (x / 4) + cos (log 4x)]
y = cos (log x) cos (log 4) − [1 / 2] * [cos (log x −log 4) + cos (log x + log 4)]
y = cos (log x) cos (log 4) − [1 / 2] * [2 cos (log x) cos (log 4)]
y = 0
Question 7: Let f : R → R be defined by f (x) = 2x + |x|, then f (2x) + f (−x) − f (x) = _______.
Solution:
f(x) = 2x + |x|
f(2x) = 2(2x) + |2x| = 4x + 2|x|
f(-x) = -2x + |-x| = -2x + |x|
-f(x) = -2x + (-|x|) = -2x – |x|
Hence, f(2x) + f(-x) – f(x) = 4x + 2|x| – 2x + |x| – 2x – |x|
= 2|x|
= 2x; x ≥ 0 and -2x; x < 0
Question 8: If f (x) = cos [π2] x + cos[−π2] x, where [x] stands for the greatest integer function, then find the function of the right angle.
Solution:
f (x) = cos [π2] x + cos[−π2] x
f (x) = cos (9x) + cos (−10x) {since π = 3.14}
= cos (9x) + cos (10x)
= 2 cos (19x / 2) cos (x / 2)
Now, right angle = π/2
So, f (π / 2) = 2 cos (19π / 4) cos (π / 4)
f (π / 2) = 2 *(−1 / √2) * (1/ √2)
= −1
Question 9: If
, for every real number, then what is the minimum value of f?
Solution:
Let
= 1 − (2 / [x2 + 1]) [Because [x2 + 1] > 1 also (2 / [x2 + 1]) ≤ 2]
So 1 − [2 / [x2 + 1]] ≥ 1 − 2;
−1 ≤ f (x) < 1
Thus, f (x) has a minimum value equal to -1.
Question 10: The function f : R → R defined by f (x) = ex is ________.
Solution:
Function f: R → R is defined by f (x) = ex.
Let x1, x2 ∈ R and f (x1) = f (x2) or ex1 = ex2 or x1 = x2.
Therefore, f is one-one.
Let f (x) = ex = y.
Taking log on both sides, we get x = log y.
As we know, negative real numbers have no pre-image, or the function is not onto, and zero is not the image of any real number.
Therefore, function f is one-one and into.
Question 11: If f: R → S defined by f (x) = sin x − √3 cos x + 1 is onto, then what is the interval of S?
Solution:
Given,
f (x) = sin x − √3 cos x + 1
As we know, the range of the function f(x) = a cos x + b sin x + c is given by:
c – √(a2 + b2) ≤ f(x) ≤ c + √(a2 + b2)
− √[1 + (√−3)2] ≤ (sin x − √3 cos x) ≤ √[1 + (√−3)2]
−2 ≤ (sin x − √3 cos x) ≤ 2
−2 + 1 ≤ (sin x − √3 cos x + 1) ≤ 2 + 1
−1 ≤ (sin x − √3 cos x + 1) ≤ 3
i.e., range = [−1, 3]
For f to be onto, the interval of S = [−1, 3].
More Related PDF Download
Maths Topicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download |
English Topicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download |
GK/GS/GA Topicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download |
Reasoning Topicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download |
Indian Polity Free PDF > Click Here To Download |
History Free PDF > Click Here To Download |
Computer Topicwise Short Tricks > Click Here To Download |
EnvironmentTopicwise Free PDF > Click Here To Download |
UPSC Notes > Click Here To Download |
SSC Notes Download > Click Here To Download |
JEE Main Maths , Relations And Functions Questions With Solutions
Question 12: What is the domain of the function
?
Solution:
Given,
Let g (x) = sin−1 (3 − x)
−1 ≤ 3 −x ≤ 1
Domain of g(x) is [2, 4] and let h (x) = log [|x| − 2]
|x|− 2 > 0
|x| > 2
x < −2 or x > 2
(−∞, −2) ∪ (2, ∞)
Also, log(|x| – 2) ≠ 0
|x| – 2 ≠ 1
|x| ≠ 3
We know that (f / g) (x) = f(x) / g(x) ∀ x ∈ D1 ∩ D2 − {x ∈ R : g (x) = 0}
Domain of f (x) = (2, 4] − {3} = (2, 3) ∪ (3, 4].
Question 13: If f (x) = a cos (bx + c) + d, then what is the range of f (x)?
Solution:
f (x) = a cos (bx + c) + d ..(i)
As we know, -1 ≤ cos θ ≤ 1
For minimum, cos (bx + c) = −1
From (i), f (x) = −a + d = (d − a)
For maximum, cos (bx + c) = 1
From (i), f (x) = a + d = (d + a)
Range of f (x) = [d − a, d + a]
Alternatively,
-1 ≤ cos(bx + c) ≤1
-a ≤ a cos(bx + c) ≤ a
-a + d ≤ a cos(bx + c) + d ≤ a + d
Range of f(x) = [d – a, a + d]
Question 14: The function f: R → R is defined by f (x) = cos2 x + sin4x for x ∈ R, then what is f (R)?
Solution:
f (x) = cos2 x + sin4x
y = f (x) = cos2 x + sin2x (1 − cos2x)
y = cos2 x + sin2x − sin2x cos2x
y = 1 − sin2x cos2x
y = 1 − [1 / 4] * [sin22x]
3 / 4 ≤ f (x) ≤ 1, (Because 0 ≤ sin22x ≤ 1)
f (R) ∈ [3/4, 1]
Question 15: If f (x) = 3x − 5, then f−1(x) is _____________.
Solution:
Let f (x) = y ⇒ x = f−1 (y).
Hence, f (x) = y = 3x − 5
⇒f−1 (y) = x
f is one-one and onto, so f−1 exists and is given by f−1 (x) = [x + 5] / [3]
TOPIC RELATED PDF DOWNLOAD
Maths Formula pdf– Download Pdf
Maths Gyan sutra – Download Pdf
pdfdownload.in will bring you new PDFs on Daily Bases, which will be updated in all ways and uploaded on the website, which will prove to be very important for you to prepare for all your upcoming competitive exams.
The above PDF is only provided to you by PDFdownload.in, we are not the creator of the PDF, if you like the PDF or if you have any kind of doubt, suggestion or question about the same, please send us on your mail. Do not hesitate to contact. [email protected] or you can send suggestions in the comment box below.
Please Support By Joining Below Groups And Like Our Pages We Will be very thankful to you.
- Facebook Page : https://www.facebook.com/onlyupsc/
TEGS:-all important formulas for jee mains 2022 pdf chemistry,important formulas for jee mains maths pdf,formula book for jee maths,jee mains physics all formulas pdf,formula sheet for jee mains maths,chemistry important formulas for jee mains pdf,formula sheet for jee mains physics,best formula book for jee